검증 요구사항
1. 타입 검증
- 가격, 수량에 문자가 들어가면 검증 오류 처리
2. 필드 검증
- 상품명: 필수, 공백X
- 가격: 1000원 이상, 100만원 이하
- 수량: 최대 9999개
3. 특정 필드의 범위를 넘어서는 검증
- 가격 * 수량의 합은 10,000원 이상
현재까지 폼 입력시 검증하는 로직은 없다. 클라이언트가 항상 옳은 방식으로 이용할리도 없다. 따라서 검증을 해줘야 한다.
검증을 하지 않으면 클라이언트는 어떤 부분에서 잘못된 입력을 했는지 알기 어렵기 때문에 고객이탈의 가능성이 높아진다.
고객이 입력한 데이터를 유지한 상태로 어떤 오류가 발생했는지 친절하게 알려줘야 한다.
컨트롤러의 중요한 역할 중 하나는 HTTP 요청이 정상인지 검증하는 것이다.
- 클라이언트 검증은 조작할 수 있으므로 보안에 취약하다.
- 서버만으로 검증하면, 즉각적인 고객 사용성이 부족해진다.
- 둘을 적절히 섞어서 사용하되 최종적으로 서버 검증은 필수이다.
- API 방식을 사용하면 API 스펙을 잘 정의해서 검증 오류를 API 응답 결과에 잘 남겨주어야 한다.
Validation - V1
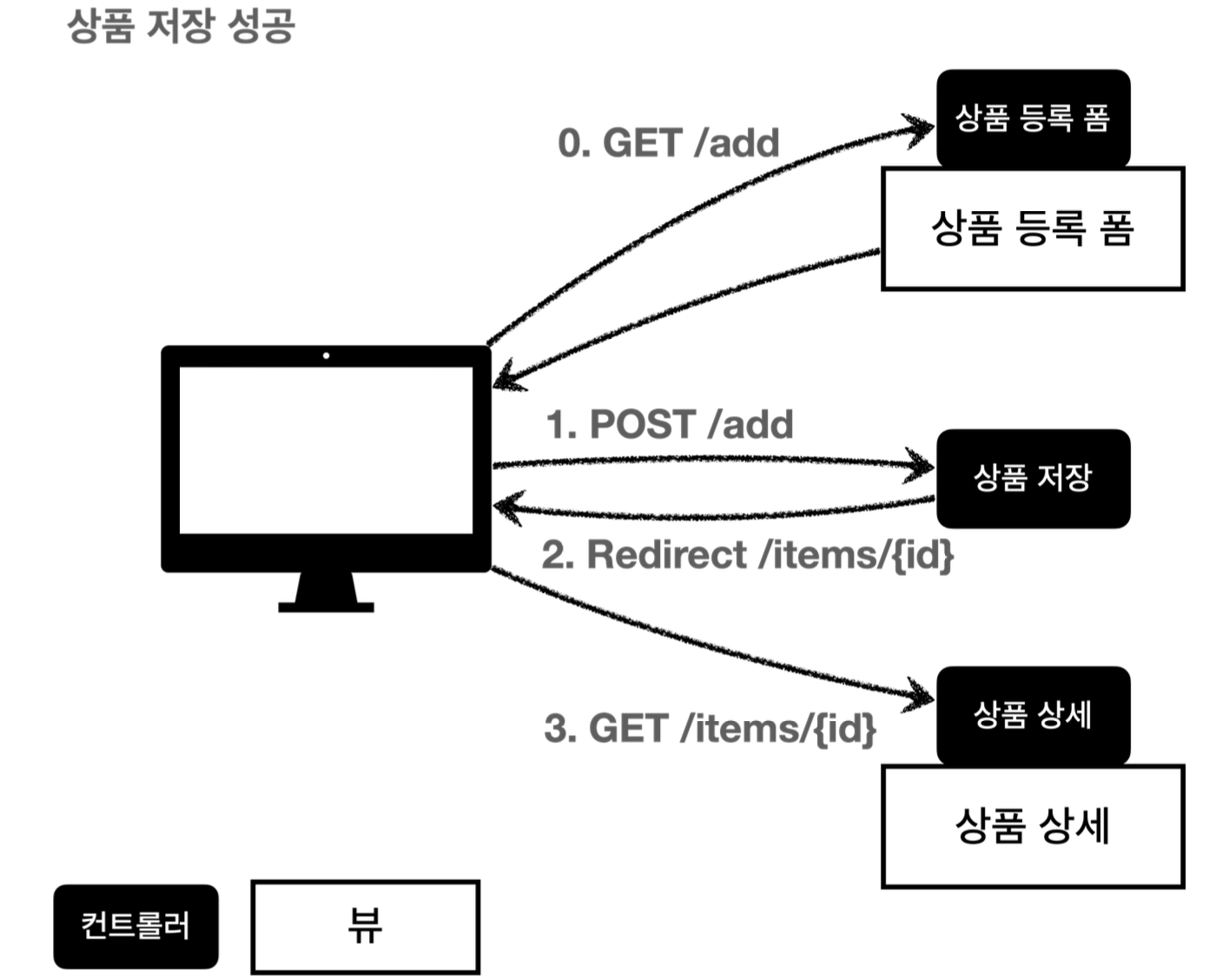
사용자가 상품 등록 폼에서 정상 범위의 데이터를 입력하면, 서버에서는 검증 로직이 통과 -> 상품 저장 -> 상품 상세 redirect
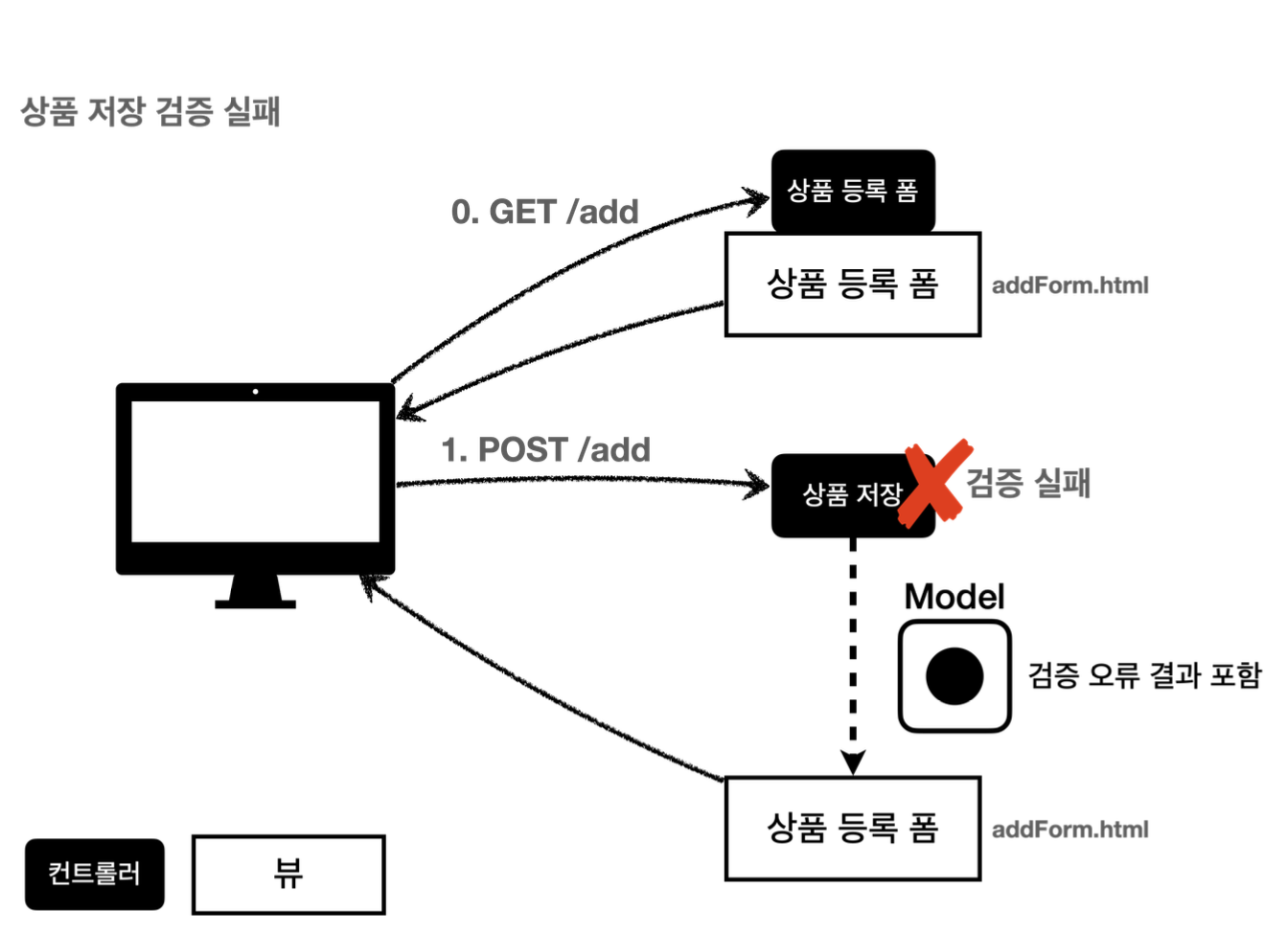
고객이 정상 범위 밖의 데이터를 입력한 경우 상품 등록 폼을 다시 보여주고, 어떤 값을 잘못입력했는지 알려줘야한다.
검증 직접 처리 - 개발
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/validation/v1/items")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class ValidationItemControllerV1 {
private final ItemRepository itemRepository;
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItem(@ModelAttribute Item item, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes, Model model) {
// 검증 오류 결과를 보관
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<>();
// 검증 로직
if (!StringUtils.hasText(item.getItemName())) {
errors.put("itemName", "상품 이름은 필수입니다.");
}
if (item.getPrice() == null || item.getPrice() < 1000 || item.getPrice() > 1000000) {
errors.put("price", "가격은 1,000원 ~ 1,000,000원 까지 허용합니다.");
}
if (item.getQuantity() == null || item.getQuantity() >= 9999) {
errors.put("quantity", "수량은 최대 9,999 까지 허용합니다.");
}
// 특정 필드가 아닌 복합 룰 검증
if (item.getPrice() != null && item.getQuantity() != null) {
int resultPrice = item.getPrice() * item.getQuantity();
if (resultPrice < 10000) {
errors.put("globalError", "가격 * 수량의 합은 10,000원 이상이어야 합니다. 현재값 = " + resultPrice);
}
}
// 검증에 실패하면 다시 입력 폼으로
if (!errors.isEmpty()) { // 부정의 부정 = 긍정. 리팩토링 신경써서하기
log.info("errors={}", errors);
model.addAttribute("errors", errors);
return "validation/v1/addForm";
}
// 성공 로직
Item savedItem = itemRepository.save(item);
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("itemId", savedItem.getId());
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("status", true);
return "redirect:/validation/v1/items/{itemId}";
}
}
검증 오류 보관
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<>();
이곳에 검증시 오류가 발생하면 어떤 오류가 발생했는지 정보를 담아둔다.
검증 로직
if (!StringUtils.hasText(item.getItemName())) {
errors.put("itemName", "상품 이름은 필수입니다.");
}
if (item.getPrice() == null || item.getPrice() < 1000 || item.getPrice() > 1000000) {
errors.put("price", "가격은 1,000원 ~ 1,000,000원 까지 허용합니다.");
}
if (item.getQuantity() == null || item.getQuantity() >= 9999) {
errors.put("quantity", "수량은 최대 9,999 까지 허용합니다.");
}
검증 오류가 발생하면, errors에 담아둔다. 이 때 어떤 필드에서 어떤 오류가 발생했는지 구분하기 위해 에러 발생 필드명을 key로 사용한다. 이렇게 되면 이후 뷰에서 이 데이터를 사용해 고객에게 에러 메세지를 전달할 수 있다.
특정 필드의 범위를 넘어서는 검증 로직
// 특정 필드가 아닌 복합 룰 검증
if (item.getPrice() != null && item.getQuantity() != null) {
int resultPrice = item.getPrice() * item.getQuantity();
if (resultPrice < 10000) {
errors.put("globalError", "가격 * 수량의 합은 10,000원 이상이어야 합니다. 현재값 = " + resultPrice);
}
}
특정 필드를 넘어서는 오류를 처리해야 할 수도 있다. 이 때는 필드 이름을 넣을 수 없으므로 globalError라는 key로 관리한다.
검증 실패 시 다시 입력 폼으로
// 검증에 실패하면 다시 입력 폼으로
if (!errors.isEmpty()) { // 부정의 부정 = 긍정. 리팩토링 신경써서하기
log.info("errors={}", errors);
model.addAttribute("errors", errors);
return "validation/v1/addForm";
}
만약 검증에 실패한 경우 에러 메세지를 출력하기 위해 model에 errors를 담고 있고, 입력 폼이 있는 뷰 템플릿으로 보낸다.
addForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
.field-error {
border-color: #dc3545;
color: #dc3545;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2 th:text="#{page.addItem}">상품 등록</h2>
</div>
<form action="item.html" th:action th:object="${item}" method="post">
<div th:if="${errors?.containsKey('globalError')}">
<p class="field-error" th:text="${errors['globalError']}">전체 오류 메세지</p>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemName" th:text="#{label.item.itemName}">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" th:field="*{itemName}"
th:class="${errors?.containsKey('itemName')} ? 'form-control field-error': 'form-control'"
class="form-control" placeholder="이름을 입력하세요">
<div class="field-error" th:if="${errors?.containsKey('itemName')}" th:text="${errors['itemName']}">상품명 오류
</div>
</div>
<div>
<label for="price" th:text="#{label.item.price}">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" th:field="*{price}"
th:class="${errors?.containsKey('price')} ? 'form-control field-error': 'form-control'"
class="form-control" placeholder="가격을 입력하세요">
<div class="field-error" th:if="${errors?.containsKey('price')}" th:text="${errors['price']}">가격 오류
</div>
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity" th:text="#{label.item.quantity}">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" th:field="*{quantity}"
th:class="${errors?.containsKey('quantity')} ? 'form-control field-error': 'form-control'"
class="form-control" placeholder="수량을 입력하세요">
<div class="field-error" th:if="${errors?.containsKey('quantity')}" th:text="${errors['quantity']}">수량 오류
</div>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" type="submit" th:text="#{button.save}">상품 등록</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg"
onclick="location.href='items.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/validation/v1/items}'|"
type="button" th:text="#{button.cancel}">취소</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
.field-error {} 부분은 에러 메세지를 빨간색으로 표시하기 위해 추가한 css
오류 메세지는 errors에 내용이 있을때만 출력하면 된다. 타임리프의 th:if를 사용하면 조건에 만족할 때만 해당 HTML 태그를 출력할 수 있다.
Safe Navigation Operator
errors?.가 무엇이냐? errors가 null일 경우에, errors.containskey()를 호출하는 순간 NPE가 발생한다. null을 호출한거나 다름없으니까. errors?.는 errors가 null일 경우에 NPE가 발생하는 대신 null을 반환하는 문법이다. 스프링EL 문법이니 궁금하면 찾아봐라
필드 오류 처리
<input type="text" th:classappend="${errors?.containsKey('itemName')} ? 'field-error' : _"
class="form-control">
classappend를 사용해서 해당 필드에 오류가 있으면 field-error라는 클래스 정보를 더해서 폼의 색깔을 빨간색으로 강조하게 할 수 있다. (편의 기능) 값이 없다면 _ (No-Operation) 사용해서 아무것도 하지 않음.
필드 오류처리 메세지
<div class="field-error" th:if="${errors?.containsKey('itemName')}" th:text="${errors['itemName']}">
상품명 오류</div>
마찬가지로 errors에 내용이 있을때만 출력되게 th:if를 사용했다. 앞쪽에 있는 class="field-error"는 css 적용 코드.
정리
- 검증 오류 시 입력 폼을 다시 보여준다. (모델의 값이 남아있는)
- 검증 오류를 클라이언트에게 자세하게 알려줄 수 있다.
- 검증 오류가 발생해도 고객이 입력한 데이터가 유지된다.
남은 문제점
- 뷰 템플릿에서 중복처리가 많다.
- 타입 에러 처리가 안된다. price, quantity에 String이 들어올 경우 400 에러 발생. 입력폼이 아닌 400 에러 페이지가 출력되기 때문에 고객은 에러내용을 알기 어려움
- 결국 고객이 입력한 값도 어딘가에 보관되어야 함
BindingResult1
스프링이 제공하는 검증 오류 처리 방법이다. 핵심은 BindingResult이다.
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/validation/v2/items")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class ValidationItemControllerV2 {
private final ItemRepository itemRepository;
@GetMapping
public String items(Model model) {
List<Item> items = itemRepository.findAll();
model.addAttribute("items", items);
return "validation/v2/items";
}
@GetMapping("/{itemId}")
public String item(@PathVariable long itemId, Model model) {
Item item = itemRepository.findById(itemId);
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "validation/v2/item";
}
@GetMapping("/add")
public String addForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("item", new Item());
return "validation/v2/addForm";
}
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV1(@ModelAttribute Item item,
BindingResult bindingResult,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes,
Model model) {
// 검증 오류 결과를 보관
// 검증 로직
if (!StringUtils.hasText(item.getItemName())) {
bindingResult.addError(
new FieldError(
"item",
"itemName",
"상품 이름은 필수입니다."));
}
if (item.getPrice() == null
|| item.getPrice() < 1000
|| item.getPrice() > 1000000) {
bindingResult.addError(
new FieldError(
"item",
"price",
"가격은 1,000원 ~ 1,000,000원 까지 허용합니다."));
}
if (item.getQuantity() == null || item.getQuantity() >= 9999) {
bindingResult.addError(
new FieldError(
"item",
"quantity",
"수량은 최대 9,999 까지 허용합니다."));
}
// 특정 필드가 아닌 복합 룰 검증
if (item.getPrice() != null
&& item.getQuantity() != null) {
int resultPrice = item.getPrice() * item.getQuantity();
if (resultPrice < 10000) {
bindingResult.addError(
new ObjectError(
"item",
"가격 * 수량의 합은 10,000원 이상이어야 합니다. 현재값 = "));
}
}
// 검증에 실패하면 다시 입력 폼으로
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) { // 부정의 부정 = 긍정. 리팩토링 신경써서하기
log.info("errors={}", bindingResult);
return "validation/v2/addForm";
}
// 성공 로직
Item savedItem = itemRepository.save(item);
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("itemId", savedItem.getId());
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("status", true);
return "redirect:/validation/v2/items/{itemId}";
}
@GetMapping("/{itemId}/edit")
public String editForm(@PathVariable Long itemId, Model model) {
Item item = itemRepository.findById(itemId);
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "validation/v2/editForm";
}
@PostMapping("/{itemId}/edit")
public String edit(@PathVariable Long itemId, @ModelAttribute Item item) {
itemRepository.update(itemId, item);
return "redirect:/validation/v2/items/{itemId}";
}
}
addItemV1 메서드에 BindingResult bindingReuslt가 추가되었다. 파라미터 위치는 반드시 @ModelAttribute 뒤에 와야한다.
@ModelAttribute의 정보와 연계되어있기 때문이다.
public FieldError(String objectName, String field, String defaultMessage) {}
FieldError의 구조
- objectName : @ModelAttribute의 이름
- field : 오류가 발생한 필드 이름
- defaultMessage : 오류 기본 메세지
글로벌 오류
bindingResult.addError(
new ObjectError(
"item",
"가격 * 수량의 합은 10,000원 이상이어야 합니다. 현재값 = "));
}
글로벌 오류는 ObjectError 객체를 생성해서 bindingResult에 담아두면 된다. 글로벌은 필드가 없다.
타임리프 스프링 검증 오류 통합 기능
타임리프는 스프링의 BindingResult를 활용해서 편리하게 검증 오류를 표현하는 기능을 제공한다.
- @fields : @fields로 BindingReuslt가 제공하는 오류에 접근할 수 있다.
- th:errors : 해당 필드에 오류가 있는 경우 태그를 출력한다. (th:if의 편의기능)
- th:errorclass : th:field 에서 지정한 필드에 오류가 있으면 class 정보를 추가한다. (이렇게 해서 css를 적용시켰다.)
BindingResult2
- 스프링이 제공하는 검증 오류를 보관하는 객체이다.
- BindingResult가 있으면, @ModelAttribute에 데이터 바인딩 시 오류가 발생해도 컨트롤러가 호출된다.
(예: Integer타입에 String이 들어가면 오류 정보를 (FieldError) BindingResult에 담아서 컨트롤러를 정상 호출함. 만약 BindingResult가 없다면 400에러 페이지이동)
BindingReuslt에 검증 오류를 적용하는 방법
- @ModelAttribute 객체에 타입 오류등으로 바인딩이 실패하는 경우 스프링이 FieldError를 생성해서 넣어줌 (위 내용)
- 개발자가 직접 넣어줌 (우리가 구현했던 코드)
- Validator 사용 -> 후에 설명
BindingResult와 Errors
BindingResult는 인터페이스이고, Errors 인터페이스를 상속받고 있다.
실제 넘어오는 구현체는 BeanPropertyBindingResult 인데, 둘 다 구현하고 있으므로 BindingResult 대신 Errors를 사용해도 된다. 하지만 Errors는 구현체가 아니므로 기능이 적으니 BindingReuslt를 사용하면 된다. 주로 이걸 쓰기도 하고.
현재 코드에서 오류가 발생하면 고객이 입력한 데이터가 모두 사라진다. 이걸 해결해보자.
FieldError, ObjectError
고객이 잘못된 값을 입력하더라도 폼에 입력한 값이 남아있게 변경해보자.
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV2(@ModelAttribute Item item,
BindingResult bindingResult,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes,
Model model) {
// 검증 오류 결과를 보관
// 검증 로직
if (!StringUtils.hasText(item.getItemName())) {
bindingResult.addError(new FieldError(
"item",
"itemName",
item.getItemName(),
false, null, null,
"상품 이름은 필수입니다."));
}
}
public FieldError(String objectName, String field, @Nullable Object rejectedValue,
boolean bindingFailure, @Nullable String[] codes,
@Nullable Object[] arguments, @Nullable String defaultMessage) {}
FieldError는 이전 코드에서 사용한 생성자 말고 한가지가 더 있다.
- rejectedValue : 사용자가 입력한 값 (거절된 값)
- bindingFailure : 타입 오류같은 바인딩 실패인지, 검증 실패인지 구분하는 값
- codes : 메세지 코드
- arguments : 메세지에서 사용하는 인자
- defaultMessage : 기본 오류 메세지
(ObjectError도 유사하게 두가지 생성자를 제공한다. 궁금하면 코드 참고)
@ModelAttribute에 데이터가 바인딩되는 시점에 오류가 발생하면 모델 객체에 사용자 입력값을 유지하기 힘들다. 필드에 숫자가 아닌 문자가 입력된다면 Integer 타입에 문자를 보관할 방법이 추가로 필요하게 되는데 번거롭다. 그래서 오류가 발생한 사용자 입력값을 보관하는 별도의 방법이 rejectedValue를 사용하는 것이다.
rejectedValue : 오류 발생시 사용자 입력값을 저장하는 필드이다.
bindingFailure는 타입 오류같은 바인딩이 실패했는지 여부를 적어주면 된다. 위에선 바인딩이 실패하지 않았기에 false를 사용했다.
th:field는 정상 작동 시 모델 객체의 값을 사용하지만, 에러 발생시 FieldError에서 보관한 값을 사용해서 값을 출력한다. 그래서 rejectedValue가 사용되는 것이다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컬렉션 프레임워크 - Map, Stack, Queue (1) | 2025.01.21 |
|---|---|
| 컬렉션 프레임워크 - Set (1) | 2025.01.20 |
| 컬렉션 프레임워크 - HashSet (0) | 2025.01.18 |
| 컬렉션 프레임워크 - 해시(Hash) (1) | 2025.01.16 |
| 컬렉션 프레임워크 - List (1) | 2025.01.13 |
