API 예외처리 - 시작
HTML 페이지의 경우 지금까지 했던것처럼 4xx, 5xx와 같은 오류 페이지만 있으면 대부분 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
그런데 API의 경우는 다르다. 오류 페이지는 단순히 고객에게 오류 페이지를 보여주고 끝이지만, API는 각 오류 상황에 맞는 오류 응답 스펙을 정하고, JSON으로 데이터를 내려주어야 한다.
API 예외 컨트롤러
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionController {
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
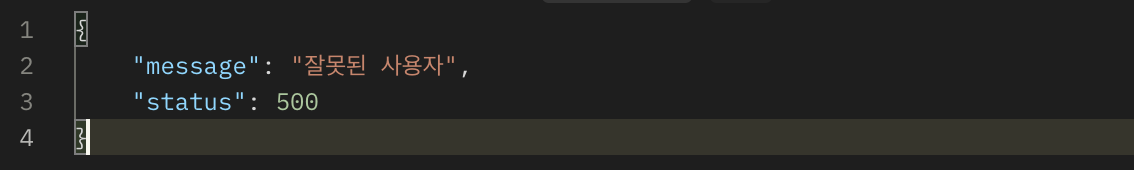
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello" + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
단순히 회원을 조회하는 기능이다. URL에 전달된 id값이 ex이면 예외가 발생한다.
이 상태로 postman으로 테스트하면 JSON 형식이 아닌 우리가 미리 만들어둔 오류 페이지 HTML이 반환된다.
@RequestMapping(value = "/error-page/500", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> errorPage500Api(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.info("API errorPage 500");
HashMap<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
Exception ex = (Exception) request.getAttribute(ERROR_EXCEPTION);
result.put("status", request.getAttribute(ERROR_STATUS_CODE));
result.put("message", ex.getMessage());
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE);
return new ResponseEntity<>(result, HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode));
}
ErrorPageController에 API응답을 추가했다.
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE 코드를 보고 Accept 값에 맞게 application/json이 호출된다.
결국 클라이언트가 받고 싶은 미디어타입이 json이면 이 컨트롤러의 메서드가 호출된다.
ResponseEntity를 사용하기 때문에 MessageConverter가 동작해 json으로 변환되어 반환된다.
API 예외 처리 - 스프링 부트 기본 예외처리
스프링부트가 제공하는 BasicErrorController로 기본 오류 방식을 사용할 수 있다.
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity(status);
} else {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
}
- errorHtml()는 반환타입이 ModelAndView이다. accept 헤더값이 text/html인 경우에 errorHtml()을 호출해서 view 제공
- error()는 반환타입이 ResponseEntity, text/html 그 외의 경우 호출되고 즉 바디에 JSON 데이터를 반환 (MessageConverter 작동)
이해안가서 다시 정리
예외 발생! -> WAS(톰캣)에서 캐치 후 /error로 forward -> 이때 /error를 보고 basicErrorController 실행 -> 예외 처리
basicErrorController는 스프링부트 실행시점에 스프링 빈으로 생성됨
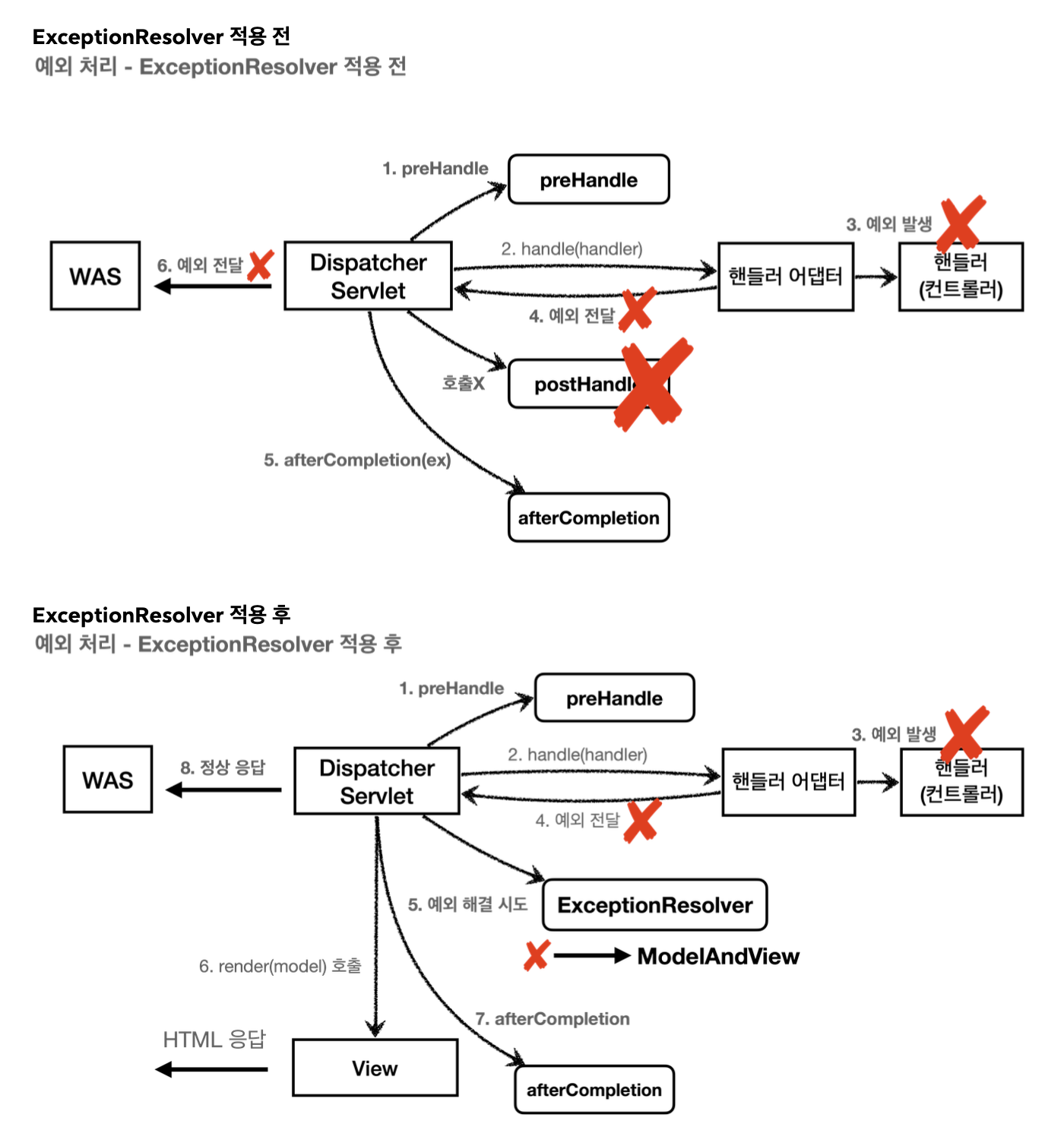
API 예외처리 - HandlerExceptionResolver
예외가 발생해 서블릿을 넘어 WAS까지 전달되면 HTTP 상태코드가 500으로 처리된다. 발생하는 예외에 따라서 400, 404 등 다른 상태코드로 처리하고, 오류 메세지, 형식등을 API마다 다르게 처리하고 싶다.
상태코드 변환
IllegalArgumentException을 처리하지 못해서 컨트롤러 밖으로 넘어가는 일이 발생하면 400에러로 처리하고싶다. 어떻게 해야할까?
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionController {
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello" + id);
}
}
if (id.equals("bad"))를 추가했다. bad로 요청 시 IllegalArgumentException이 발생한다.
이렇게만 쓰면 안되고 HandlerExceptionResolver를 사용해야한다.
package hello.exception.resolver;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
public class MyHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
log.info("IllegalArgumentException resolver to 400");
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, ex.getMessage());
return new ModelAndView();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("resolver ex", e);
}
return null;
}
}
ExceptionResolver가 ModelAndView를 반환하는 이유는 try,catch 하듯이 Exception을 처리해서 정상 흐름처럼 변경하려는 목적이다. 이름 그대로 exception을 resolver(해결)하는것이 목적이다.
여기서는 IllegalArgumentException이 발생하면 response.sendError(400)을 호출하고, 빈 ModelAndView를 반환한다.
반환 값에 따른 동작 방식
- 빈 ModelAndView : 빈 ModelAndView를 반환하면 뷰를 렌더링하지않고 정상 흐름으로 서블릿이 리턴된다.
- ModelAndView 지정 : View, Model 정보를 지정해서 반환하면 뷰를 렌더링 한다.
- null : 널을 반환하면 다음 ExceptionResolver를 찾아서 실행. 없다면 예외처리가 안되고 예외를 서블릿 밖으로 던진다. (500)
* 빈 ModelAndView를 반환한 경우 뷰를 렌더링 하지 않는다고 했다. 이럴 때 고객은 어떤 화면을 보나?
WAS가 내부적으로 에러 처리 흐름을 태운다. 톰캣은 /error로 BaiscErrorController 실행 -> JSON 또는 HTML 에러페이지 반환
그래서 고객은 400에러 응답이나 기본 에러화면을 보게됨
API 예외 처리 - HandlerExceptionResolver 활용
예외가 발생하면 WAS까지 예외가 던져지고, WAS에서 오류 페이지 정보를 찾아서 다시 /error로 호출하는 과정은 생각해보면 너무 복잡하다. ExceptionResolver를 활용하면 예외가 발생했을 때 이 과정을 생략하고 여기에서 마무리할 수 있다.
package hello.exception.exception;
public class UserException extends RuntimeException {
public UserException() {
super();
}
public UserException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public UserException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public UserException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected UserException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
예외 추가 (user-ex)
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionController {
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello" + id);
}
UserHandlerExceptionResolver 추가
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
resolvers.add(new MyHandlerExceptionResolver());
resolvers.add(new UserHandlerExceptionResolver());
}@Slf4j
public class UserHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof UserException) {
log.info("UserException resolver to 400");
String acceptHeader = request.getHeader("accept");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST);
if ("application/json".equals(acceptHeader)) {
Map<String, Object> errorResult = new HashMap<>();
errorResult.put("ex", ex.getClass());
errorResult.put("message", ex.getMessage());
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(errorResult);
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(result);
return new ModelAndView();
} else {
// text/html
return new ModelAndView("error/500");
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("resolver ex", e);
}
return null;
}
}
흐름 정리
UserException 던짐 -> 예외가 DispatcherServlet까지 전파 -> 등록해둔 HandlerExceptionResolver 목록을 순서대로 조회 -> UserHandlerExceptionResolver가 instanceof UserException에서 매칭되어 처리-> 빈 ModelAndView 반환 -> WAS 정상흐름
*objectMapper는 Map을 JSON 문자열로 직렬화해준다.
API 예외 처리 - 스프링이 제공하는 ExceptionResolver1
스프링 부트가 기본으로 제공하는 ExceptionResolver
HandlerExceptionResolverComposite에 다음 순서로 등록
1. ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
2. ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
3. DefaulthandlerExceptionResolver
1번은 자주 사용하니 뒤에 설명
2번은 HTTP 상태 코드를 지정해준다.
3번은 스프링 내부 기본 예외를 처리한다.
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
예외에 따라서 HTTP 상태코드를 지정해주는 역할을 한다.
- @ResponseStatus가 달려있는 예외
- REsponseSTatusException 예외
package hello.exception.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, reason = "error.bad")
public class BadRequestException extends RuntimeException {
}
@ResponseStatus 어노테이션을 적용하면 HTTP 상태코드가 변경된다.
BadRequestException 예외가 컨트롤러 밖으로 넘어가면 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 예외가 해당 어노테이션을 확인해서 오류코드를 HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST로 변경하고 메세지도 담는다.
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 코드를 확인하면 결국 response.sendError()를 호출하는것을 확인할 수 있다.
sendError(400)을 호출했기 때문에 WAS에서 다시 오류페이지를 요청한다. (/error)
여기서 이해 안됐던점 정리
ExceptionResolver를 사용해 빈 ModelAndView를 반환하면 WAS에서 정상흐름으로 판단해야하지 않나? 왜 /error를 요청하나?
- DispatcherServlet에서 WAS로 예외를 전달하지 않는것은 맞다. 하지만 sendError()를 호출하면, 예외는 안올라왔어도 응답 상태에 에러라는 플래그가 찍히기 때문에, WAS는 그 플래그를 보고 에러 디스패치 (DispatcherType.ERROR)로 /error 요청으로 forward -> DispatcherServlet -> BasicErrorController 실행 -> 최종 에러 응답
ResponseStatusException
@ResponseStatus는 개발자가 직접 변경할 수 없는 예외에는 적용할 수 없다. 어노테이션을 직접 넣어야하는데 내가 코드를 수정할 수 없는 라이브러리의 예외 코드같은곳에는 적용할 수 없다. 추가로 어노테이션을 사용하기 때문에 동적으로 변경도 어렵다.
이때는 ResponseStatusException을 사용하면 된다.
@GetMapping("/api/response-status-ex2")
public String responseStatusEx2() {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "error.bad", new IllegalArgumentException());
}
API 예외 처리 - 스프링이 제공하는 ExceptionResolver2
이번에는 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver를 살펴보자.
대표적인 예로 파라미터 바인딩 시점에 타입이 맞지 않으면 TypeMismatchException이 발생하는데, 이 경우 예외가 발생했기 때문에 그냥 두면 서블릿 컨테이터까지 오류가 올라가고, 결과적으로 500에러가 발생한다.
그런데 파라미터 바인딩 에러는 대부분 클라이언트가 잘못된 요청을 해서 발생하는 문제이다. HTTP에서는 이런 경우 상태코드를 400을 사용하도록 되어있다.
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver는 이것을 500이아니라 400으로 변경한다.
코드는 생략. 궁금하면 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 내부를 살펴보기
API 예외 처리 - @ExceptionHandler
웹 브라우저에 HTML 화면을 제공할 때 오류가 발생하면 BasicErrorController를 사용하는게 편하다.
이때 단순히 5xx, 4xx 관련된 오류 화면을 보여주면 된다.
그런데 API는 각 시스템 마다 응답의 모양도 다르고, 스펙도 다르다. 예외 상황에 단순히 오류 화면을 보여주는것이 아니라, 예외에 따라서 다른 데이터를 출력해야 할 수도 있다. 한마디로 세밀한 제어가 필요하다.
지금까지 해본 방식으로는 API 예외를 다루기는 쉽지 않다.
API 예외처리의 어려운 점
- handlerExceptionResolver를 떠올려보면 ModelAndView를 반환해야 했다. 이것은 API응답에는 필요없다.
- API 응답을 위해서 HttpServletResponse를 넣었다. 일일이 설정하기 너무 번거롭고 불편하다.
- 특정 컨트롤러에서만 발생하는 예외를 별도로 처리하기 어렵다. 예를들어 회원을 처리하는 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 RuntimeException 예외와 상품을 관리하는 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 동일한 RuntimeException 예외를 서로 다른 방식으로 처리하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
@ExceptionHandler
스프링은 API 예외 처리문제를 해결하기위해 @ExceptionHandler를 제공한다. 이것이 ExceptionhandlerExceptionResolver이다.
스프링은 이를 기본으로 제공하고, ExceptionResolver중에서도 우선순위가 가장 높다. 실무에서는 대부분 이 기능을 사용한다.
ErrorResult
package hello.exception.exhandler;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResult {
private String code;
private String message;
}
ApiExceptionV2Controller
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class APiExceptionV2Controller {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
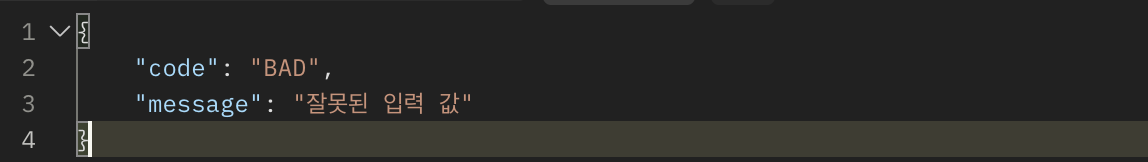
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHAndler(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionhandler] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandler(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
@GetMapping("/api2/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello" + id);
}
@GetMapping("/api2/response-status-ex1")
public String responseStatusEx1() {
throw new BadRequestException();
}
@GetMapping("/api2/response-status-ex2")
public String responseStatusEx2() {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "error.bad", new IllegalArgumentException());
}
@GetMapping("/api2/default-handler-ex")
public String defaultException(@RequestParam Integer data) {
return "ok";
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
@ExceptionHandler 예외처리 방법
어노테이션을 선언하고, 해당 컨트롤러에서 처리하고싶은 예외를 지정해주면 된다. 해당 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생하면 이 메서드가 호출된다. 참고로 지정한 예외 또는 그 예외의 자식까지 다 잡을 수 있다.
(Exception은 모든 예외의 부모라서 맨 마지막에 호출됨)
IllegalArgumentException 처리 실행 흐름 (위 코드)
- 컨트롤러 호출 결과 IllegalArgumentException 예외가 컨트롤러 밖으로 던져짐
- 예외가 발생했으므로 ExceptionResolver 작동. 가장 우선순위가 높은 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 실행
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver는 해당 컨트롤러에 IllegalArgumentException을 처리할 수 있는 @ExceptionHandler 있는지 확인
- 있으니까 illegalExHandle() 실행. @RestController 이므로 이 메서드에도 @ResponseBody 적용됨. 따라서 HTTP 컨버터가 사용되고, 응답이 JSON으로 반환
- @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)를 지정했으므로 상태코드는 HTTP 400.
UserException 처리 실행 흐름
- @ExceptionHandler에 예외를 지정하지 않으면 해당 메서드 파라미터를 사용. 여기서는 UserException 사용
- ResponseEntity를 사용해서 HTTP 메세지 바디에 직접 응답. (HTTP 컨버터 사용)
ResponseEntity를 사용하면 응답코드를 동적으로 변경 가능.
Exception 처리 실행흐름
- throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용") 이 코드가 실행되면서 컨트롤러 밖으로 RuntimeException 던져짐
- Runtime은 exception의 자식클래스 이므로 이 메서드가 호출됨.
- @ResponseStatus()로 500응답
참고로 mav를 리턴해서 오류화면을 응답할수도 있다.
API 예외 처리 - @ControllerAdvice
@Exceptionhandler를 사용해서 예외를 깔끔하게 처리할 수 있게 되었지만, 정상 코드와 예외처리 코드가 하나의 컨트롤러에 섞여있다. @ControllerAdvice 또는 @RestControllerAdvice를 사용하면 둘을 분리할 수 있다.
package hello.exception.exhandler.advice;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExControllerAdvice {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHAndler(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionhandler] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandler(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
}
package hello.exception.api;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class APiExceptionV2Controller {
@GetMapping("/api2/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello" + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
기능이 분리가 되었다.
@ControllerAdvice
- @ControllerAdvice는 대상으로 지정한 여러 컨트롤에 @ExceptionHandler, @InitBinder 기능을 부여해준다.
- @ControllerAdvice에 대상을 지정하지 않으면 글로벌로 적용된다.
- @RestControllerAdvice, @ControllerAdvice는 @ResponseBody 유무의 차이이다.
대상 컨트롤러 지정 방법
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = RestController.class)
- 특정 어노테이션이 있는 컨트롤러를 지정한다.
@ControllerAdvice("org.example.controllers")
- 해당 패키지와 그 하위에 있는 컨트롤러를 지정한다.
@ControllerAdvice(assignableType = {ControllerInterface.class, AbstractController.class})
- 특정 클래스를 지정한다.
실무에서도 사용하는 기능이다. 잘 알아두자
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파일 업로드 (0) | 2025.09.23 |
|---|---|
| 스프링 타입 컨버터 (0) | 2025.09.21 |
| 예외처리와 오류 페이지 (0) | 2025.09.19 |
| 로그인 처리2 - 필터, 인터셉터 (0) | 2025.09.18 |
| 로그인 처리1 - 쿠키, 세션 (1) | 2025.09.17 |
